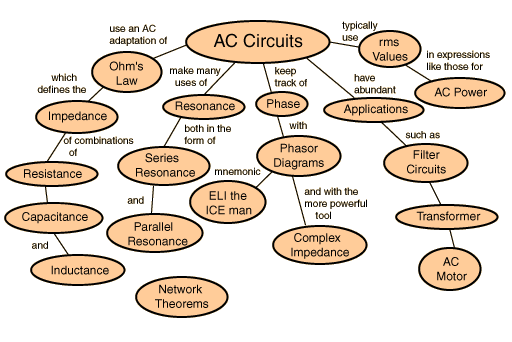
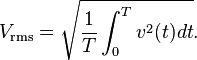Alternating Circuit (AC Circuit)
Wednesday, 19 December 2012
Saturday, 15 December 2012
varying emf by mechanically rotating a loop of wire in an external magnetic field, a sinusoidally varying electromagnetic force could be obtained in the rotating loop of wire.
alternating current i as
Ԑ = ωAB sin ωt
or
Ԑ = Ԑmax sin ωt
where
Ԑmax = ωAB
ω is the angular speed of rotating coil, A is the cross-sectional area of the coil, B is the magnetic field that the coil is rotated through.
the resulting alternating current in the coil was found to be
i = (Ԑmax /R) sin ωt
ω related to the frequency of the alternating current by
ω = 2∏f
The effective current and voltage in an AC circuit
- current, i start from 0 increase in one direction until reaches max value i(max)
- decrease to 0 and increase again in the opposite direction
- increase negatively to -i(max)
alternating current i as
i = imax sin(2∏ft)
effective current ieff is defined as a constant current that generates heat in a resistor R at the same rate as an alternating current
i =  = 0.707imax
= 0.707imax
voltage,
V = imax Rsin(2∏ft), imax R = Vmax
hence,
V = Vmax (2∏ft)
Veff = 
Saturday, 8 December 2012
The first alternator to produce alternating current was a dynamo electric generator based on Michael Faraday's principles constructed by the French instrument maker Hippolyte Pixii in 1832. Pixii later added a commutator to his device to produce the (then) more commonly used direct current. The earliest recorded practical application of alternating current is by Guillaume Duchenne, inventor and developer of electrotherapy. In 1855, he announced that AC was superior to direct current for electrotherapeutic triggering of muscle contractions.
Mathematics of AC voltages
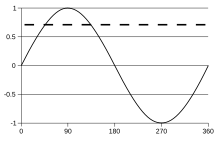
A sine wave, over one cycle (360°). The dashed line represents the root mean square (RMS) value at about 0.707
Alternating currents are accompanied (or caused) by alternating voltages. An AC voltage v can be described mathematically as a function of time by the following equation:
 ,
,
where
 is the peak voltage (unit: volt),
is the peak voltage (unit: volt), is the angular frequency (unit: radians per second)
is the angular frequency (unit: radians per second)- The angular frequency is related to the physical frequency,
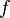 (unit = hertz), which represents the number of cycles per second, by the equation
(unit = hertz), which represents the number of cycles per second, by the equation  .
.
- The angular frequency is related to the physical frequency,
 is the time (unit: second).
is the time (unit: second).
The peak-to-peak value of an AC voltage is defined as the difference between its positive peak and its negative peak. Since the maximum value of  is +1 and the minimum value is −1, an AC voltage swings between
is +1 and the minimum value is −1, an AC voltage swings between  and
and  . The peak-to-peak voltage, usually written as
. The peak-to-peak voltage, usually written as  or
or  , is therefore
, is therefore  .
.
 is +1 and the minimum value is −1, an AC voltage swings between
is +1 and the minimum value is −1, an AC voltage swings between  and
and  . The peak-to-peak voltage, usually written as
. The peak-to-peak voltage, usually written as  or
or  , is therefore
, is therefore  .
.[edit]Power and root mean square
The relationship between voltage and the power delivered is
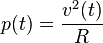 where
where 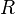 represents a load resistance.
represents a load resistance.
Rather than using instantaneous power, 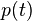 , it is more practical to use a time averaged power (where the averaging is performed over any integer number of cycles). Therefore, AC voltage is often expressed as a root mean square(RMS) value, written as
, it is more practical to use a time averaged power (where the averaging is performed over any integer number of cycles). Therefore, AC voltage is often expressed as a root mean square(RMS) value, written as  , because
, because
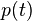 , it is more practical to use a time averaged power (where the averaging is performed over any integer number of cycles). Therefore, AC voltage is often expressed as a root mean square(RMS) value, written as
, it is more practical to use a time averaged power (where the averaging is performed over any integer number of cycles). Therefore, AC voltage is often expressed as a root mean square(RMS) value, written as  , because
, because
For a sinusoidal voltage:
The factor 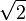 is called the crest factor, which varies for different waveforms.
is called the crest factor, which varies for different waveforms.
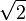 is called the crest factor, which varies for different waveforms.
is called the crest factor, which varies for different waveforms.- For a triangle waveform centered about zero
- For a square waveform centered about zero
- For an arbitrary periodic waveform
 of period
of period  :
:
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)